Logical Volume Manager (LVM) 入门
还是那句老话:
Any problem in computer science can be solved by another layer of indirection.
对于我们平时使用的文件系统,都不知道下面封装了多少层,硬盘(或者ssd)本身都内置了芯片,用来屏蔽柱面、磁道、扇区的差异。我们的服务器上还有RAID Controller,用来屏蔽物理磁盘。操作系统看到的是一个大硬盘,速度很快,其实它可能不知道下面有多少个物理磁盘,中间的写入和缓存算法,操作系统也不用关心。
如果没有硬件raid卡,我们可以通过操作系统来加一层。这样应用层序看到的还是一个大分区。
raid有个不好的地方就是,动静太大,一个raid一旦建立好以后,再修改大小可能会比较复杂。在不停机的情况下,LVM可能是一个管理磁盘的好方法。
LVM介绍
Logical Volume Manager (LVM) 利用Linux内核的device-mapper来实现存储系统的虚拟化(系统分区独立于底层硬件)。 通过LVM,你可以实现存储空间的抽象化并在上面建立虚拟分区(virtual partitions),可以更简便地扩大和缩小分区,可以增删分区时无需担心某个硬盘上没有足够的连续空间。
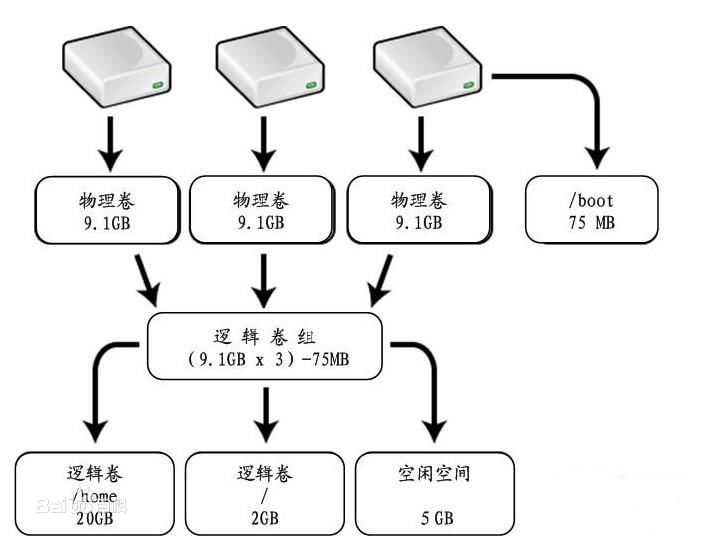
LVM中有几个需要仔细理解的感念:
- 物理存储介质(PhysicalStorageMedia):指系统的物理存储设备:磁盘,如:/dev/hda、/dev/sda等,是存储系统最底层的存储单元。
- 物理卷(Physical Volume,PV):指磁盘分区或从逻辑上与磁盘分区具有同样功能的设备(如RAID),是LVM的基本存储逻辑块,但和基本的物理存储介质(如分区、磁盘等)比较,却包含有与LVM相关的管理参数。
- 卷组(Volume Group,VG):类似于非LVM系统中的物理磁盘,其由一个或多个物理卷PV组成。可以在卷组上创建一个或多个LV(逻辑卷)。
- 逻辑卷(Logical Volume,LV):类似于非LVM系统中的磁盘分区,逻辑卷建立在卷组VG之上。在逻辑卷LV之上可以建立文件系统(比如/home或者/usr等)。
- 物理块(Physical Extent,PE):每一个物理卷PV被划分为称为PE(Physical Extents)的基本单元,具有唯一编号的PE是可以被LVM寻址的最小单元。PE的大小是可配置的,默认为4MB。所以物理卷(PV)由大小等同的基本单元PE组成。
- 逻辑块(Logical Extent,LE):逻辑卷LV也被划分为可被寻址的基本单位,称为LE。在同一个卷组中,LE的大小和PE是相同的,并且一一对应。
他们的关系如图: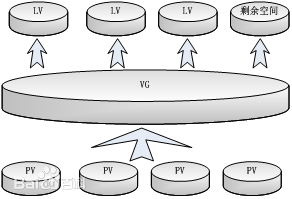
理解了上面的几个名词(记住英文),运行lvm help看一下:
Available lvm commands:
Use 'lvm help <command>' for more information
config Display and manipulate configuration information
devtypes Display recognised built-in block device types
dumpconfig Display and manipulate configuration information
formats List available metadata formats
help Display help for commands
lvchange Change the attributes of logical volume(s)
lvconvert Change logical volume layout
lvcreate Create a logical volume
lvdisplay Display information about a logical volume
lvextend Add space to a logical volume
lvmchange With the device mapper, this is obsolete and does nothing.
lvmconfig Display and manipulate configuration information
lvmdiskscan List devices that may be used as physical volumes
lvmsadc Collect activity data
lvmsar Create activity report
lvreduce Reduce the size of a logical volume
lvremove Remove logical volume(s) from the system
lvrename Rename a logical volume
lvresize Resize a logical volume
lvs Display information about logical volumes
lvscan List all logical volumes in all volume groups
pvchange Change attributes of physical volume(s)
pvresize Resize physical volume(s)
pvck Check the consistency of physical volume(s)
pvcreate Initialize physical volume(s) for use by LVM
pvdata Display the on-disk metadata for physical volume(s)
pvdisplay Display various attributes of physical volume(s)
pvmove Move extents from one physical volume to another
lvpoll Continue already initiated poll operation on a logical volume
pvremove Remove LVM label(s) from physical volume(s)
pvs Display information about physical volumes
pvscan List all physical volumes
segtypes List available segment types
systemid Display the system ID, if any, currently set on this host
tags List tags defined on this host
vgcfgbackup Backup volume group configuration(s)
vgcfgrestore Restore volume group configuration
vgchange Change volume group attributes
vgck Check the consistency of volume group(s)
vgconvert Change volume group metadata format
vgcreate Create a volume group
vgdisplay Display volume group information
vgexport Unregister volume group(s) from the system
vgextend Add physical volumes to a volume group
vgimport Register exported volume group with system
vgmerge Merge volume groups
vgmknodes Create the special files for volume group devices in /dev
vgreduce Remove physical volume(s) from a volume group
vgremove Remove volume group(s)
vgrename Rename a volume group
vgs Display information about volume groups
vgscan Search for all volume groups
vgsplit Move physical volumes into a new or existing volume group
version Display software and driver version information
无非就是对pv、lv、vg的增删改查而已。对于查看,可以用pvs、lvs、vgs,或者pvdisplay、lvdisplay、vgdisplay,增加用exten,删除用remove。所以命令很好理解。
示例
给/dev/mapper/centos-home 扩容
我们的服务器上新增加了两块硬盘,希望可以在线给/dev/mapper/centos-home扩容。
#查看一下现在的情况
df -hT
文件系统 类型 容量 已用 可用 已用% 挂载点
/dev/mapper/centos-root xfs 50G 2.7G 48G 6% /
devtmpfs devtmpfs 16G 0 16G 0% /dev
tmpfs tmpfs 16G 0 16G 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs tmpfs 16G 41M 16G 1% /run
tmpfs tmpfs 16G 0 16G 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/mapper/centos-home xfs 866G 275G 591G 32% /home
/dev/sda1 xfs 497M 167M 330M 34% /boot
tmpfs tmpfs 3.2G 0 3.2G 0% /run/user/0
#创建物理分区
fdisk /dev/sdb
t
8e
#创建PV
lvm pvcreate /dev/sdb1
#把PV添加到VG
vgextend centos /dev/sdb1
#修改LV的大小
lvextend -l +100%FREE /dev/mapper/centos-home
#让OS识别新的大小
#对于xfs分区(前面df -hT可以查看类型)
xfs_growfs /dev/mapper/centos-home
#如果是ext4分区可以用
resize2fs